Gambia
The trial in the adulterated syrups affair which caused the death of children last year in The Gambia resumed Tuesday (Nov. 07), before the Banjul High Court.
The families of the victims, grouped within the AKI association, are awaiting convictions at the end of this trial which was delayed in July and then postponed in October after the five defendants did not attend the hearing.
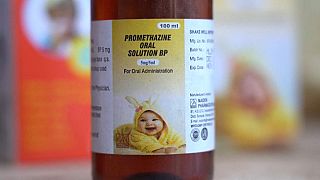
Some 70 children aged 5 and under died in 2022 from kidney failure after taking the over-the-counter medicines.
Nineteen plaintiffs are suing five defendants -- company Maiden Pharmaceuticals, local distributor Atlantic Pharmaceuticals, the Medical Controls Agency, the Ministry of Health and Attorney General Dawda A. Jallow -- to demand they admit that the children were killed by consuming contaminated medicines.
Maiden Pharmaceuticals has denied the allegations.
At some point, the Gambian health authorities cited E.coli bacteria as a possible cause of the deaths.
In July, a government taskforce in The Gambia announced its finding that four cough syrups imported from India were responsible for the deaths.
Plaintiffs are demanding about $230,000 per child in damages.
They are also suing for an admission that the MCA failed in its statutory duty to regulate the quality and safety of medicines.
The Gambian government also said it was exploring options to take legal action against the Indian manufacturer.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), lab tests found "unacceptable amounts" of diethylene glycol and ethylene glycol, which are commonly used as antifreeze and can be fatal when ingested.
Beginning in September last year, The Gambia ordered a recall of several cough and cold medications, as well as all products manufactured by the Indian laboratory Maiden Pharmaceuticals from which the adulterated syrups originated.
In the aftermath of the scandal, India launched an investigation and shut down the Maiden Pharmaceuticals plant last October.
And The Gambia's president Barrow vowed to create a national laboratory to test for drug quality and food safety, which doens't exist in the country.
In January, the WHO announced a call for "immediate and coordinated action" to eradicate non-compliant and falsified medicines, in particular tainted cough syrups linked to the deaths of 300 children in Gambia, Indonesia and Uzbekistan.












01:45
Detainees released in Burundi as part of effort to reduce overcrowding in prisons
01:28
Dozens of health workers on trial in Turkey accused of causing infant deaths
Go to video
Ghana's Supreme Court restores NPP's Parliamentary majority ahead of December election
01:02
Imane Khelif files legal complaint over reports alleging she has XY chromosomes
01:14
Nigerian children could face death penalty for taking part in protests
01:25
WHO says almost a million mpox vaccines have been allocated to Africa